Two Phase Thermal Solution Guide
Overview
Over several decades, Boyd has been a leading innovator of two phase cooling with superior solutions for everything from consumer electronics to space applications. Boyd leveraged this experience and expertise to develop this Reference Guide to help you understand two phase technologies and find the right solution for your applications. This article explains the most popular two phase thermal solutions, integrations, and customizations as well as what to consider when selecting the best technology for your application. Utilizing heat pipes, vapor chambers, or thermosiphons can be the best way to optimize cooling with higher performance in more compact geometries for best total value.

Introduction
As electronics around the world demand more power functionality, and reliability, heat remains one of the major to barriers to achieving maximized performance and to realizing major innovations. Every industry, especially Mobile, Medical, Telecommunications and IoT are developing new applications that are lightweight, multi functional, high power, and required to be more reliable. Engineers are struggling to effectively handle excess heat as consumers demand smaller, thinner, more powerful devices with more options and capabilities.
Two phase cooling is rapidly gaining more popularity in solving these issues. These are technologies are especially ideal for heat spreading for faster dissipation, light weighting, higher reliability and lifetime, but their most significant benefit is design flexibility and the ability to easily integrate them into a system to vastly improve cooling efficiency and capacity. Active air cooling or liquid cooling alone are often too large and cumbersome and come with their own complications such as acoustics, weight, and vibration. By integrating or designing out more active components, two phase can also solve acoustic and vibration issues,
While most engineers are most familiar with heat pipes, which provide the benefits of to phase cooling in a more linear and very flexible for factor, there are several major types of two phase technologies that can handle more heat or feature their own specific benefits and features. Vapor chambers transfer heat in a planar geometry allowing for my uniform heat spreading. Thermosiphons do not require a wicking structure and can be more cost efficient by using gravity to move fluid. Meanwhile, Immersion Cooling is becoming more popular in high power markets as they can work with higher heat loads.
The following guide will touch on each of these technologies and the benefits and considerations when utilizing them to cool your applications.
Two Phase Cooling Basics
Passive
Two-phase technologies have no moving parts and operate on the laws of thermodynamics and capillary forces, making these solutions silent, efficient and extremely reliable with no inner wear and tear. This enables longer product lifetimes with no degradation in performance, improved acoustics and longer warranty periods due to lower temperatures.
Highly Efficient
Heat pipes and vapor chambers have a conductivity of 10X – 200X that of solid thermally conductive materials such as copper, aluminum, and graphite. They also tend to be much lighter and use less material than solid conductors. This enables solutions to transport more heat with less weight in the same volume, or, vice-versa, heat pipes can transport the same amount of heat in a much smaller weight and volume than solid solutions.
Vapor chambers are especially effective as they are utilized for planar, X-Y spreading while heat pipes are typically relegated to enhancing heat sink base spreading or increasing their fin efficiency. Spreading the heat from single or multiple chips over the increased surface area of vapor chambers creates more uniform heat transfer and improves cooling.
The high efficiency and efficacy of two phase technologies enable lower, more regulated touch temperatures. Improved heat spreading also improves user safety and comfort and decreases the likelihood of overheating if the device is left running constantly or for longer than average use times. This mitigates user complaints of device failure due to overheating or even catching fire. May lessen or eliminating the use of fans, two phase assemblies can mitigate acoustic and vibration issues.
Cost Efficient
Less weight, material usage and improved performance also generate cost savings. Better cooling allows for smaller solutions and BOM savings or more room for more components and added functionality. Cost savings can be further augmented with advanced engineering and Design for Manufacture (DFM) techniques like those utilized at Boyd. Through effective thermal modeling and testing for optimal performance and designing specifically for scalable manufacturing from prototypes to high volume, cost savings can be further improved and passed on to the end customer. Thermosiphon technologies can provide addition cost efficiency when gravity is fixed. The do not have a wicking structure, and negating that manufacturing step saves time and money.

Increase Design Flexibility
The wicking structure allows vapor chambers and heat pipes to operate in any orientation, including against gravity with the evaporator higher than the condenser, with minimal effects on performance. This ability makes them ideal for mobile, portable, and consumer electronics that need to operate in various orientations including landscape, portrait and inverted.
In addition to multiple orientations, these solutions offer increased design flexibility for unique and high tolerance geometries. While heat pipes can be bent, flattened, and arranged to optimize heat transfer and flow; vapor chambers can accommodate various device heights and through holes for mounting. Utilizing alternate materials, such as titanium or stainless steel, increases the level of customization, offering better performance and key market differentiation.
As Boyd continues to innovate, our techniques have evolved to make the best use of design and materials to further enhance application performance and optimize size and weight. Boyd two-phase innovations incorporate new manufacturing processes and advanced additive manufacturing practices to further improve cost savings, ease of manufacture, design flexibility and overall thermal performance.
Key innovations include:
- Reaching an unprecedented level of wick customizations and performance matching to highly specific or varying application and user requirements.
- Proprietary methods for enabling unique and complex geometries in a way that traditional methods could not produce easily or with the required level of cost efficiency.
- Advanced manufacturing techniques to integrate multiple geometries and features in a single process to reduce fabrication times. This enables cost savings in labor and materials as well as shorter lead times.
- New and improved technologies such as Immersion Cooling Boiler Plates to Advanced Ultra Thin Vapor Chambers.
- The consideration and optimization given to thermal management has become a key selling point for many of our customers marketing new technologies. Heat is one of the final barriers to end-user device innovation.
|
Technology |
When to Use |
When Not to Use |
Key Benefits |
Key Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Heat Pipes |
When experiencing poor fin efficiency When a heat sink has enough overall convective cooling performance but experiences hot spots that need to be spread within the base. When it is simpler to implement multiple heat pipes rather than a vapor chamber. When heat needs to be transported far from the heat source |
When the distance between the heat source and area to dissipate the heat is short ~<70mm. When the heat source is a similar size to a heat sink base and fin efficiency is acceptable. When the number of heat pipes needed are too high and it is more efficient to use a vapor chamber. |
Can be included into most heat sink types with little effort to augment or upgrade their performance. Are cost effective and meet performance needs while reducing weight or volume of the thermal solution. |
Mobile Devices |
|
Vapor Chambers |
When heat sink has enough cooling performance, but as hot spots that make the heat sink base less effective. When performance requirements warrant maximum spreading performance and does not allow enough heat pipes to be embedded physically or economically |
For bases that have an excessive number of thru holes and pockets. When adding heat pipes will not meet the requirements. |
Allows ideal heat spreading over the base of a heat sink making all fins attached to it as efficient as possible. Enables much higher effective thermal conductivities vs graphite May allow heat spreading through and entire 3D volume when a 3Dvc is used |
Mobile devices including AR / VR |
|
Thermosiphons |
When the power and distance between a heat source and the finned heat exchanger surface or condenser is such that heat pipes are not practical due to excessive number of heat pipes needed vs. 2 tubes of a thermosiphon. When power needs to be distributed over a 3D volume within a finned condenser more effectively that placing heat pipes in a fin stack |
When the heat source is above the condenser region with respect to gravity. When orientation may change, or other forces may act on the thermosiphon (not recommended for moving platforms such as automotive or aerospace). |
Offers the ability to move heat over a longer distance that HPs or VCs, as long as gravity can be used to return the fluid. Allows solutions to use a combination of copper and aluminum to minimize weight and cost while still being able to add copper in high heat flux regions. |
Enterprise (Server, Networking, and Outdoor Telecom Equipment) |
|
Immersion Cooling |
When direct liquid cooling is considered but plumbing on each PCB is impractical. When air or liquid cooling does not main the same local ambient conditions to each chip (shadowing) leaving to over design of the cooling solution. **When high heat flux components are used a proper boiling plate with applied BEC must be used. |
Where air cooling is sufficient Where facilities do not already have the infrastructure in place to contain fluid For small mobile devices |
Fluid allows constant local ambient conditions for all electronics Allows cooling or components at lower heat fluxes with simple heat sinks or in some cases no heat sinks at all. Minimizes system thermal design with focus on a few high power or high heat flux components |
Enterprise server |
Heat Pipes
Heat pipe assemblies combine the proven reliability of passive two phase heat transport with a variety of other thermal management technologies to generate effective, long lasting cooling solutions. Boyd has been innovating and fabricating heat pipe solutions for more than five decades. Our experience enables us to design and fabricate effective and long-lasting cooling solutions that operate under the most demanding environmental conditions.
Ductile copper walls and wick enable bending or flattening to meet an application’s thermal and geometric requirements. This can be used to reduce overall height, increase surface contact, or route heat pipes around keep-out areas like mounting hardware.
Heat pipes can be embedded in other technologies for faster heat spreading or utilized within a system to transport heat from the heat source to where is can safely dissipated. Copper-water heat pipes are often integrated into thermal management assemblies to improve effective conductivity and efficiency, improving overall system performance.
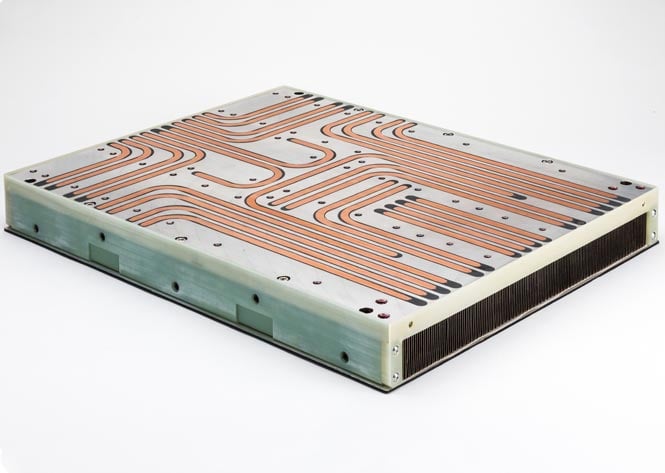
Heat Pipe Variations
- Alternate Materials & Fluids
- Allow for Cryogenic Options, Extreme Temperature Changes, High Heat
- Flexible
- Use of a bellows allows frequent folding and movement with no degradation to heat pipe performance
- Ultra-Thin
- Near flat heat pipes that allow for extremely low profile applications.
- Loop Heat Pipes
- Transport and control the direction of heat over long distances up to 23 meters.
Typical Parameters for Copper-Water Heat Pipes
Length: 75mm – 500mm**
Diameter: 3mm – 9.5mm**
Material: High Purity Copper
Fluid: Water**
Typical Non-Operational Temperature Range: -55° to 180°C (Water)
- Wick
- Sintered Copper Powder
- Axially Grooved
- Wire Mesh Screen
Maximum Heat Flux: >300 W/cm2
Lifespan: up to 20 years
** Larger sizes and different working fluids are available based on application use

Vapor Chambers
Vapor chambers leverage high heat transport capabilities of two phase cooling in a planar format, making vapor chambers assemblies ideal components when spreading high heat densities or heat loads across a larger surface. This enables increased and more uniform heat spreading, which is ideal when optimizing heat sink performance
Boyd integrates vapor chambers into specialized air cooled heat sinks to improve heat distribution to each of the fins, improving the overall performance of the heat sink. Boyd is consistently innovating to develop and manufacture them in a variety of materials and working fluids. This includes our Ultra-Thin Copper-Water and Stainless Steel-Water Vapor Chambers for high heat density, high strength cooling in applications such as PEM fuel cells and low profile consumer and mobile electronics.
Additional Considerations & Benefits
- More uniform heat spreading for cooler device temperatures
- Reduces heat sink volume and overall thermal solution weight by using fins more effectively (or use the same volume to increase heat load/device performance)
- Reduce thermal solution complexity by using one vapor chamber as opposed to multiple heat pipes with complex bent geometries
- Fins such as Zipper Fin or Folded Fin may be mounted directly to vapor chambers by soldering.
- Vapor chambers may also be inserted into pockets with the extruded or cast heat sink base by soldering or thermal epoxy.
Advanced 3D Vapor Chambers
3D Vapor Chambers are typically used where extremely high performance is required within a local heat sink volume at the heat source. These solutions are specialized air-cooled heat sinks with vapor chambers incorporated into the base and fins for fast heat spreading and more efficient heat dissipation. These innovative assemblies solve challenges for isothermal, high performance cooling where space is limited, and efficiency is key.
In addition to advanced, integrated design and assembly, Boyd vapor chamber innovations also include utilizing advanced working fluids. Although water is still the primary working fluid and highly effective, some applications such as those used in aerospace and extreme environments have requirements that make water unsuitable. This is especially true in environments with extreme temperatures or thermal cycling. It is imperative to match fluid and material properties to allow for proper functionality. Using incompatible materials can lead to corrosion, shorter lifetimes or loss of performance.


Thermosiphons
Thermosiphons offer higher power heat transportation vs heat pipes or vapor chambers, but as they are wickless, they need a known orientation with respect to gravity to operate. For additional cost savings, Boyd offers advanced engineering and streamlined manufacturing that enables one shot brazing. Boyd has also developed loop thermosiphon solutions that offer passive liquid cooling for more reliable high-power cooling. Thermosiphons are often more complete system solutions as compared to heat pipes and vapor chambers which are most often components integrated into a in a larger thermal system.
There are two main types of thermosiphons:
- Air to Air Heat Exchanger that rejects heat from one air flow stream to another utilizing the thermosiphon working fluid
- Remote heat ejection from a local component to ambient air using the thermosiphon working fluid to reject heat using a remote condenser.
Immersion Cooling
Immersion cooling systems include a boiling plate attached to high heat flux devices such as CPU’s and GPU’s that are immersed in a dielectric fluid. These plates include a BEC (boiling enhancement coating) that initiates boiling of the fluid with a small temperature difference. The bubbles that boil up in the fluid bring the heat to the surface and reject the heat from the system when it condenses on a heat exchanger or cooling coil type condenser.
Boyd’s Immersion Cooling Boiler Plates are extremely high performance, differentiated with a boiling enhancement coating (BEC) optimized with high boiling capacity and low temperature rise to ensure component temperatures are maintained below their maximum limits.
Materials: Copper for high heat flux and Aluminum for lower heat flux components.

Design Considerations
Two phase solutions offer increased design flexibility and are extremely customizable. It is vital to consider your options when optimizing your solution.
Wicking Structures
In addition to sintering, wicking options include grooves and screen-mesh options. Grooves are extruded with the tube. Screens or mesh are rolled and inserted into the pipe along the interior wall.
Working Fluids
Water is typically the best choice due to its excellent heat of vaporization and working temperature range that are ideal for electronic cooling applications. For specialize applications requiring extremely low or high temperatures, other fluids may be considered. Each working fluid noted has a set of compatible materials that can be used for the outer walls of the heat pipe of vapor chamber.
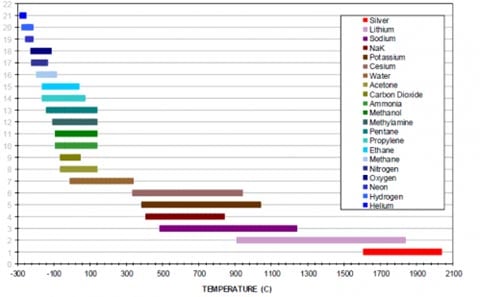
Materials
Heat pipes and vapor chambers can be manufactured in a wide range or materials and alloys, although Copper is the most common. Copper is extremely compatible with water and several other fluids, highly conductive, and is easy to manufacture. If additional strength is required, stainless steel or titanium may be selected with the latter the best choice when weight reduction is desired.
|
Material |
Tensile Strength (Mpa) |
Density |
Specific Strength (kNm/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Copper (Cu) |
220 |
8960 |
24.5 |
|
Stainless Steel (SS) |
505 |
7700 |
65.5 |
What is Next?
Boyd’s decades of innovation expertise, experience, resources and unique approach to integrating multiple technologies into a streamlined product will continue to keep the company on the forefront of innovation and improved manufacturing. If you are ready to improve or retrofit your cooling solutions or are looking to tackle new challenges for the next generation, start by contacting Boyd to learn more about two phase solutions, customizations, and other possibilities for better optimized cooling.
Related Links and Resources
Have questions? We’re ready to help!




