What is a Liquid Cold Plate?
A Liquid Cold Plate (LCP) is responsible for efficiently transferring heat from surfaces with high heat loads to the fluid used within a liquid cooling system. The performance of the liquid cold plate is critical in defining the overall effectiveness of a liquid system.
100% In-Line Testing
Reliable, leak-free cold plates produced for decades.
Push product performance with next level cooling
Outperform air cooling with effective liquid cooling plates
Optimize Direct Liquid Cooling Interfaces
Custom cold plate skylines and pedestals maximize the interface between a heat source and the cooling system for peak performance.
Highly Customizable
Optimize design for balance flow rate and pressure drop for optimized performance.
Liquid Cold Plate Solutions for e-Mobility and Transportation
(View transcript)
What Are Liquid Cold Plates?
A liquid cold plate (LCP) serves as a critical interface within a liquid cooling system, guiding pumped fluid to heat sources and transferring waste heat into the coolant for subsequent cooling. Cold plates feature a heat source mounting surface, internal passages for liquid to pass through, and an inlet and outlet. Thermal engineers optimize cold plate liquid flow path design and construction to maximize cooling within the liquid cooling system constraints like pressure drop and flow.
High Efficiency Cooling Components
Liquid cold plates act as the part of a liquid cooling system that absorbs waste heat from devices like semiconductors, microprocessors, printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs), or other power electronics and transfers it to the liquid cooling system. Optimize cooling efficiency and uphold the ideal operating temperature of electronic components by harnessing the exceptional heat-absorbing capabilities of liquid through cold plates.
Have a Question?
How do Liquid Cold Plates Work?
A cold plate by itself does not cool devices; it must be integrated into a liquid loop that includes a pump for fluid circulation and a heat exchanger to reject the heat absorbed by the cold plate.Why use Liquid Cold Plates?
Leverage the high heat capacity of liquid to quickly absorb more heat than air cooled thermal management solutions. Coldplates excel at dissipating high-density, high-output heat loads within a diverse range of system configurations, facilitating the effective transfer of heat into the liquid cooling system.

Why Choose Boyd for your Liquid Cold Plate?
Boyd’s engineers excel at developing and manufacturing high quality, compact, and durable coldplates to meet your system requirements while reducing weight and complexity. We leverage accurate performance simulations based off decades of empirical data to quickly optimize cold plate design and accelerate your design cycle. Boyd’s extensive fabrication methods and leak-free construction options help you reduce product weight, push performance, or decrease overall assembly size with high performance LCPs.
EV Battery Solutions
View our 3D interactive tool to explore Boyd’s EV battery solutions and how we drive multifaceted innovation. Click the image or the button below to immerse yourself with our EV battery solutions!Meet Application Requirements with the Right Construction
Since liquid cooling is utilized in a wide variety of applications, Boyd has developed the broadest range of liquid cold plate technologies in the thermal management industry. Our engineering team leverages the best fit technology to meet project requirements like thermal performance, flow rate, resistance and pressure drop, wetted path materials, weight, durability, and geometry.
Learn more about our most popular LCP technologies:
Stamped Liquid Cold Plates
Stamped cold plates are a lightweight cold plate construction that leverages the manufacturing efficiency of aluminum stamping one or both sides of the LCP. This approach further reduces manufacturing time and costs by streamlining flow path, mounting geometry, and other features into a single process and eliminates CNC time. Stamped cold plates can be enhanced with internal fins to boost thermal efficiency and are controlled atmosphere brazed (CAB) brazed for leak-free seals.eMobility
Electric vehicle batteries, on-board electronic, power conversion
Energy Management
Power conversion
Machined Liquid Cold Plates
Machined and brazed cold plates offer the most flow path and structural geometry customization for a heat source to liquid system interface. Optimize complex, leak-free flow channels with precision CNC machining and high-quality CAB or vacuum brazing. Boyd’s broad technology portfolio enables additional performance boost with fin inserts to further enhance heat transfer into the liquid system.Artificial Intelligence & Cloud Computing
Semiconductor and processor cooling
Industrial Process Equipment
Motor drive cooling, power conversion, laser and sensor cooling
Energy Management
Power conversion, battery energy storage systems
Round Tube Liquid Cold Plates
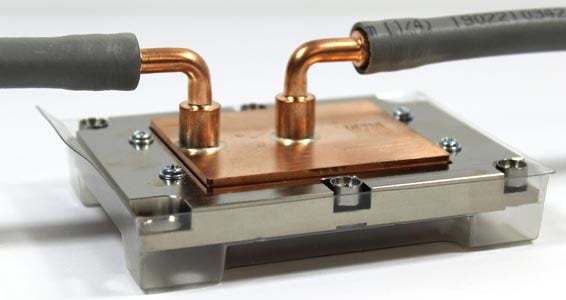
Boyd’s round tube LCPs are cost-effective component cooling for low to moderate heat loads. Tubed cold plates consist of copper or stainless-steel tubes pressed into channeled aluminum plates. Tube cooling plates are available with either continuous tube styles or a manifold style. Enhance tube cold plate performance with the addition of turbulators by 5-15%.


Industrial Process Equipment
Motor drive cooling, power conversion, laser and sensor cooling
Energy management
Power conversion
Flat Tube Manifold Liquid Cold Plates
Flat tube cold plates are ideal to cool small, high heat density components like thermoelectric coolers in limited vertical spaces. Using thin-walled aluminum multi-port extrusion (MPE) tubing, flat tube cooling plates minimize thermal resistance between the cold plate and heat source and produce surface thermal uniformity. Flat tube LCPs use more viscous fluids like ethylene glycol and water (EGW), oils, 3M Fluorinert®, and Polyalphaolefin (PAO) with their enhanced internal surface area and low pressure drop.
Telecommunications
Computer or server microprocessor cooling and test equipment thermal management
Aerospace
Lightweight avionics, motor and electronics cooling solutions in more electric aircraft (MEA), electronic heat transport to stowed radiator panels during satellite launch. They can also operate as thermal diodes to prevent backward heat leak.
Defense
Actuator-mounted electronics cooling, engine waste heat wing and cowl anti-icing, and thermal signature suppression
Liquid Cold Plate Customization
Materials
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Stainless Steel
Wetted path needs to be compatible with other components in the liquid loop. Mixing copper and aluminum leads to galvanic corrosion that decreases system performance and lifetime.
Flow Path Options
- Meso-channel
- Parallel channel
- Tube and/or manifold
Manufacturing Processes
- CNC machining
- Friction stir welding
- Stamping
- CAB brazing
- Vacuum brazing
Have questions? We’re ready to help!